If you’re planning on booking some electrical work, the chances are you’ll be hearing some words and terms that you may not be too familiar with… or that you haven’t heard since secondary school science class.
This electrical terminology guide will give you enough information for you to understand what your engineers are talking about. You may even find yourself brave enough to drop an acronym or two in conversation.
Alternating Current (AC) | An electrical current that alters its direction of flow many times per second. |
Amp / Ampere (A) | The single unit of electrical current. |
Bonding | Connections on exposed metal-work to stop electric shocks, by means of an earth connection. |
| The British Standard Requirements for Electrical Installations, previously known as IEE Wiring Regulations. This document informs of the requirements for electrical installations in the UK. |
Circuit | The action of distributing electricity, consisting of cables and accessories. |
Circuit Breaker (CB) | This device automatically breaks an electrical circuit when a fault is detected. |
Circuit Tester | This device plugs into a standard outlet to check a circuit is properly grounded. |
Conductors | Any material, substance or device that allows the flow of electricity. |
Direct Current (DC) | An electrical current that flows in one direction, e.g. Battery. |
Distribution Board (DB) | A piece of equipment that is used to connect circuits to an electricity supply. |
 |
Distribution Circuit | A circuit supplying electricity to a secondary distribution board. |
Distribution Network Operator (DNO) | The company that distributes electricity to your home. |
| A report showing the condition of your property’s existing electrical installation. |
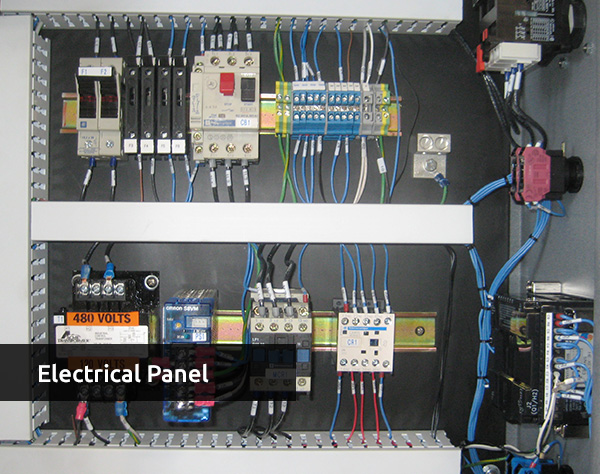
Electrical Panel | An insulated panel that is used to connect electrical wires to circuit breakers. |
 |
Extractor Fan | An electrical ventilator for bathrooms and kitchens to prevent moisture from developing. |
Extra Low Voltage | A low supply of electricity. 50V AC or less. |
Fault Finding | The act of testing circuits to see if there is a fault within the chosen electrical system. |
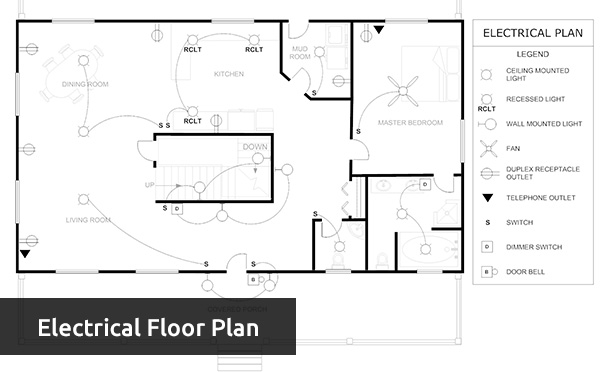
Floor Plan | A simple scaled drawing to portray rooms as seen from above |
 |
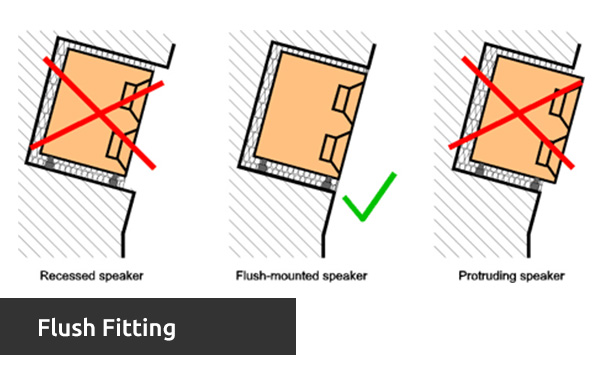
Flush | The way in which electrical accessories are sunk into the wall, so only the face place protrudes. |
 |
Fuse | A safety device that will melt the wire inside it if an excessive current flows through it. |
 |
Fuse Board | An enclosure that contains fuses for a property. |
Fused Connection Unit (FCU) | An electrical accessory containing a cartridge fuse, used to connect and protect a piece of electrical equipment. |
Hertz (Hz) | Unit of measure of electrical frequency. |
Ingress Protection (IP) | A rating system that shows how protected an enclosure is against liquids and solids. |
Insulation Resistance (IR) | The measurement of how an electrical circuit or piece of equipment is able to resist electricity leakage. |
Light-Emitting Diode (LED) | An energy efficient device that produces light when supplied with electricity, developing rapidly into a viable light source in its own right. |
 |
Live | The collective name for the conductors that carry the normal operating current. |
Live Conductors | Wires with electrical current actively running through them. |
Neutral Conductor | A conductor that under normal conditions will carry no current. |
Low Voltage | An electrical supply of between 50V AC and 1000V AC. |
Luminaire | A light fitting. |
Neon Voltage Tester | A tool used to detect if wires are live. |
Neutral (N) | A term used to describe one of the cable cores in a normal mains supply. |
 |
Ohm | A unit of measure for electric resistance. |
Ohm’s Law | V=IR where V is the voltage in volts, I is the current in amperes, and R is the resistance in ohms. |
Over Current | A condition when the normal load current is exceeded in a circuit. This may result in an overload or a short circuit. |
Overhead Wires | Wires that are above the ground. |
Overload | An over current exceeding the normal full load current of a circuit. |
Radial Circuit | A circuit set so that the cable runs from the consumer unit or fuse box to one or more accessories without returning to the source. |
| A current-activated circuit breaker used as a safety device for mains operated electrical tools and appliances that offers earth fault protection. |
Recessed Lighting | A light fixture installed into a hollow opening. Also known as a down light. |
Resistance | The property of an electrical circuit, measured in ohms, that restricts the flow of current. |
Resistive Load | An electrical load with no considerable inrush current. |
Semiconductor Fuse | A fuse that is used to protect solid-state devices. |
 |
Short Circuit | An overcurrent greater than the original full load current of a circuit. |
Short Circuit Rating | The maximum short circuit current an electrical component can sustain without excessive damage. |
Spur | A cable that supplies a socket or other accessories, which branches from a circuit. |
 |
Switch Leg | A wire connected to a power switch. |
Volt (V) | A unit of electrical pressure. |
Voltage Rating | The maximum open circuit voltage with which a fuse can be used. |
Watts | The energy consumed by an appliance per second is expressed in watts. |